[인프런/스프링 DB 2편] 5. 스프링 트랜잭션
📌 @Transactional 사용
-> 트랜잭션 프록시 적용
-> 트랜잭션 AOP 처리
1. 트랜잭션 적용 확인
1) build.gradle
plugins {
id 'java'
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '3.1.1'
id 'io.spring.dependency-management' version '1.1.0'
}
group = 'hello'
version = '0.0.1-SNAPSHOT'
java {
sourceCompatibility = '17'
}
configurations {
compileOnly {
extendsFrom annotationProcessor
}
}
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa'
compileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
runtimeOnly 'com.h2database:h2'
annotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
testImplementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
//테스트에서 lombok 사용
testCompileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
testAnnotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
}
tasks.named('test') {
useJUnitPlatform()
}
2) TxBasicTest - 트랜잭션 적용 확인
package hello.springtx.apply;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.assertj.core.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.aop.support.AopUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.TestConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionSynchronizationManager;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.*;
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
public class TxBasicTest {
@Autowired
BasicService basicService;
@Test
void proxyCheck() {
// 프록시 만들어졌는지 테스트
log.info("aop class={}", basicService.getClass());
assertThat(AopUtils.isAopProxy(basicService)).isTrue();
}
@Test
void txTest() {
// 트랜잭션 적용됐는지 테스트
basicService.tx();
basicService.nonTx();
}
@TestConfiguration
static class TxApplyBasicConfig {
@Bean
BasicService basicService() {
return new BasicService();
}
}
@Slf4j
static class BasicService {
@Transactional
public void tx() {
log.info("call tx");
boolean txActive = TransactionSynchronizationManager.isActualTransactionActive();
log.info("tx active={}", txActive);
}
public void nonTx() {
log.info("call nonTx");
boolean txActive = TransactionSynchronizationManager.isActualTransactionActive();
log.info("tx active={}", txActive);
}
}
}
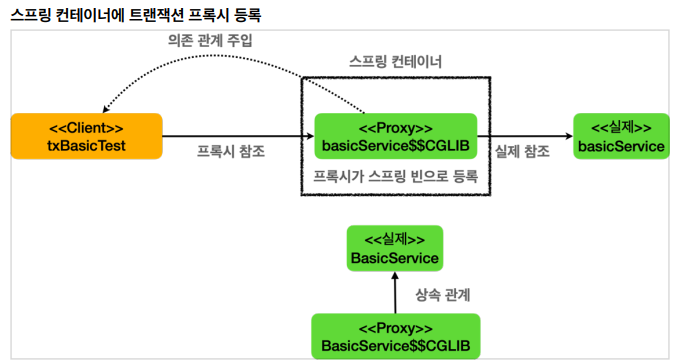
(1) proxyCheck()
- AopUtils.isAopProxy()
- @Transactional 을 특정 클래스나 메소드에 하나라도 사용 -> 스프링 트랜잭션 AOP 적용의 대상
-> 실제 BasicService 객체가 아닌, 프록시 객체가 스프링 빈에 등록 + 프록시 객체 주입
( 프록시는 BasicService를 상속해서 만들어지기 때문에 다형성 활용 -> BasicService가 부모객체)
- @Transactional 을 특정 클래스나 메소드에 하나라도 사용 -> 스프링 트랜잭션 AOP 적용의 대상

(2) txTest()
- application.properties 에 로그 추가
- 트랜잭션 시작과 종료를 명확하게 로그로 확인할 수 있음
logging.level.org.springframework.transaction.interceptor=TRACE
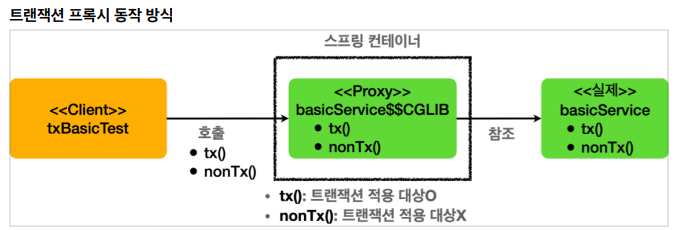
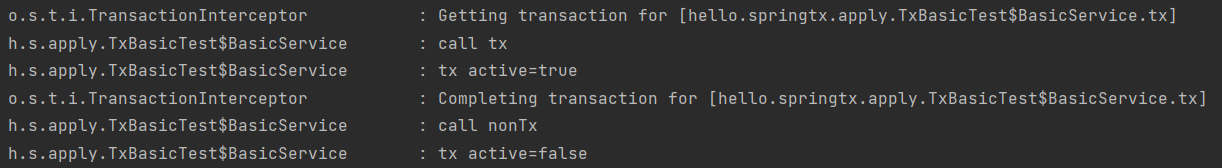
- basicService.tx() 호출
- 프록시의 tx() 호출 -> 프록시는 tx() 메소드가 트랜잭션을 사용할 수 있는지 확인 -> @Transactional 확인 -> 적용 대상 O
- 실제 basicService의 tx() 호출
- 호출이 끝나면 프록시는 트랜잭션 로직을 커밋/롤백 해서 트랜잭션 종료
- basicService.nonTx() 호출
- 프록시의 nonTx() 호출 -> 프록시는 nonTx() 메소드가 트랜잭션 사용할 수 있는지 확인 -> @Transactional 없음 -> 적용 대상 X
- 트랜잭션을 시작하지 않고, basicService의 nonTx() 호출하고 종료
- TransactionSynchronizationManager.isActualTransactionActive()
- 현재 스레드에 트랜잭션이 적용되어 있는지 확인
2. 트랜잭션 우선순위
1) TxLevelTest
package hello.springtx.apply;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.TestConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionSynchronizationManager;
@SpringBootTest
public class TxLevelTest {
@Autowired
LevelService service;
@Test
void orderTest() {
service.write();
service.read();
}
@TestConfiguration
static class TxApplyLevelConfig {
@Bean
LevelService levelService() {
return new LevelService();
}
}
@Slf4j
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
static class LevelService {
@Transactional(readOnly = false) // 기본값 (생략가능)
public void write() {
log.info("call write");
printTxInfo();
}
public void read() {
log.info("call read");
printTxInfo();
}
private void printTxInfo() {
boolean txActive = TransactionSynchronizationManager.isActualTransactionActive();
log.info("tx active={}", txActive);
boolean readOnly = TransactionSynchronizationManager.isCurrentTransactionReadOnly();
log.info("tx readOnly={}", readOnly);
}
}
}
* 스프링의 @Transactional 규칙
(1) 우선순위 규칙
더 구체적이고 자세한 것이 우선순위
- LevelService 클래스 : @Transactional(readOnly = true)
- write() 메소드 : @Transactional(readOnly = false) -> 적용
(2) 클래스에 적용하면 메소드는 자동 적용
- read() 메소드 : @Transactional 없음
- LevelService 클래스 : @Transactional(readOnly = true) -> 클래스의 트랜잭션 옵션 자동 적용
2) 결과
* write() 호출
readOnly = false 옵션 적용

* read() 호출
readOnly = true 옵션 적용

💡 인터페이스에 @Transactional 적용
1. 클래스의 메소드 (우선순위 ↑)
2. 클래스의 타입
3. 인터페이스의 메소드
4. 인터페이스의 타입
-> 별로 비추 -> 클래스에 적용할 것!
3. 🚨 트랜잭션 AOP 주의 사항
3-1. 프록시 내부 호출
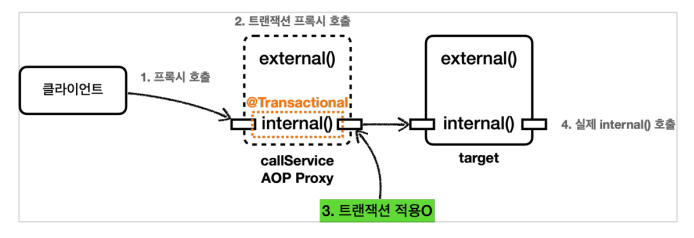
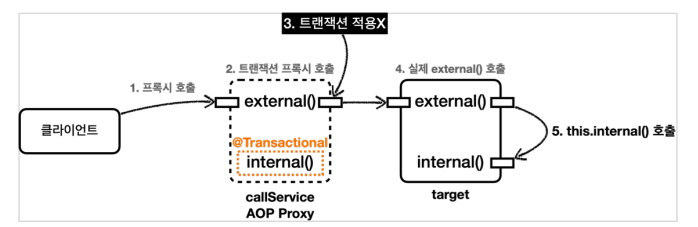
프록시 내부 호출
(1) 원래
@Transactional 사용-> 트랜잭션 AOP 적용 -> 대상 객체 대신 프록시를 스프링 빈으로 등록 + 주입 !
-> 프록시 호출 -> 프록시에서 트랜잭션 적용 -> 프록시에서 대상 객체의 메소드 호출 ! => 트랜잭션 적용 보장
(2) 내부 호출 문제
대상 객체 내부에서 자신의 메소드 호출 -> 프록시를 거치지 않고 대상 객체 직접 호출 -> 트랜잭션 적용 X
1) 트랜잭션 내부 호출 예제
package hello.springtx.apply;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.TestConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionSynchronizationManager;
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
public class InternalCallV1Test {
@Autowired
CallService callService;
@Test
void printProxy() {
log.info("callService class={}", callService.getClass());
}
@Test
void internalCall() {
callService.internal();
}
@Test
void externalCall() {
callService.external();
}
@TestConfiguration
static class InternalCallV1TestConfig {
@Bean
CallService callService() {
return new CallService();
}
}
@Slf4j
static class CallService {
public void external() {
log.info("call external");
printTxInfo();
internal();
}
@Transactional
public void internal() {
log.info("call internal");
printTxInfo();
}
private void printTxInfo() {
boolean txActive = TransactionSynchronizationManager.isActualTransactionActive();
log.info("tx active={}", txActive);
}
}
}
(1) CallService 프록시 객체 생성됐는지 확인
- @Transactional 이 하나라도 있으면 트랜잭션 프록시 객체 생성됨 !
(external()은 없지만, internal()은 있음) - 주입받은 CallService = 프록시 객체

(2) internal() 실행 - 트랜잭션 O


- callService.internal() 호출 ( = 프록시의 internal() )
- 트랜잭션 프록시 호출
- @Transactional 확인 -> 트랜잭션 적용 O
- 트랜잭션 적용 후 실제 CallService 객체의 internal() 호출
- 실제 CallService 객체의 처리 완료 후 트랜잭션 프록시가 트랜잭션 완료
(3) external() 실행 - 트랜잭션 없이, 트랜잭션이 있는 internal() 호출
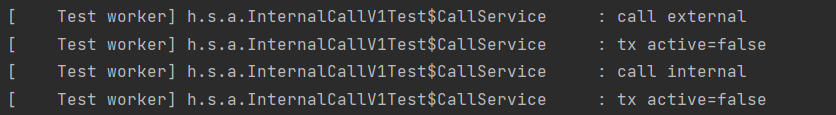

- callService.external() 호출 ( = 프록시의 external() )
- 트랜잭션 프록시 호출
- @Transactional 없음 -> 트랜잭션 적용 X
- 트랜잭션 적용 없이 실제 CallService 객체의 external() 호출
- external() 은 내부에서 자신의 internal() 호출 (this.internal()) -> 프록시 거치지 않음 -> 트랜잭션 적용 X )
=> @Tansactional을 사용하는 트랜잭션 AOP는 메소드 내부 호출에 프록시를 적용할 수 없음 !
2) 프록시 내부 호출 해결 방법 - 별도의 클래스로 분리
package hello.springtx.apply;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.TestConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionSynchronizationManager;
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
public class InternalCallV2Test {
@Autowired
CallService callService;
@Test
void printProxy() {
log.info("callService class={}", callService.getClass());
}
@Test
void externalCallV2() {
callService.external();
}
@TestConfiguration
static class InternalCallV1TestConfig {
@Bean
CallService callService() {
return new CallService(internalService());
}
@Bean
InternalService internalService() {
return new InternalService();
}
}
@Slf4j
@RequiredArgsConstructor
static class CallService {
private final InternalService internalService;
public void external() {
log.info("call external");
printTxInfo();
internalService.internal();
}
private void printTxInfo() {
boolean txActive = TransactionSynchronizationManager.isActualTransactionActive();
log.info("tx active={}", txActive);
}
}
@Slf4j
static class InternalService {
@Transactional
public void internal() {
log.info("call internal");
printTxInfo();
}
private void printTxInfo() {
boolean txActive = TransactionSynchronizationManager.isActualTransactionActive();
log.info("tx active={}", txActive);
}
}
}- InternalService 클래스로 분리 -> 메소드 내부 호출을 외부 호출로 변경
- CallService에는 트랜잭션 관련 코드 X -> 트랜잭션 프록시 적용 X
- InternalService에는 트랜잭션 코드 O -> 트랜잭션 프록시 적용 O
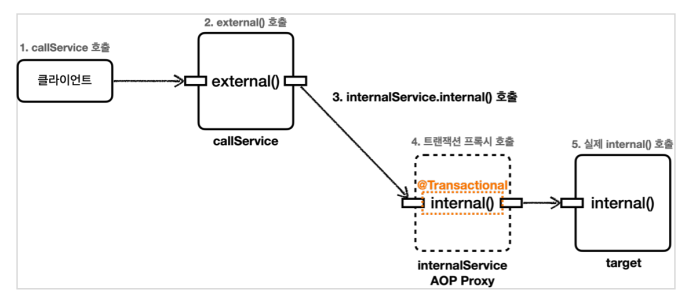
- callService.external() 호출 (실제 callService 객체)
- callService는 주입받은 internalService.internal() 호출
- @Transactional 확인 -> 트랜잭션 프록시 적용 -> 트랜잭션 적용
- 실제 internalService 객체의 internal() 호출
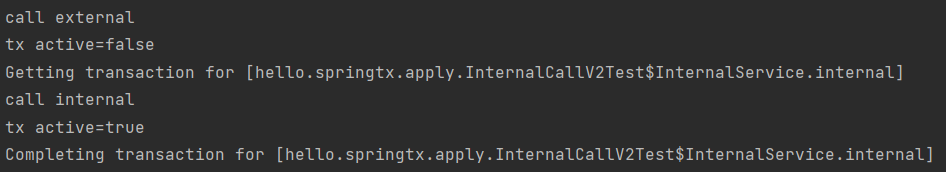
💡 public 메소드만 트랜잭션 적용
스프링 트랜잭션 AOP는 public 메소드에만 트랜잭션 적용하도록 기본 설정
public이 아닌 private, protected, package-visible 등에 @Transactional 붙어있으면 -> 트랜잭션 적용 무시
3-2. 초기화 시점과 트랜잭션 AOP 적용
스프링의 초기화 시점에는 트랜잭션 AOP가 적용되지 않을 수 있음
package hello.springtx.apply;
import jakarta.annotation.PostConstruct;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationReadyEvent;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.TestConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.event.EventListener;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionSynchronizationManager;
@SpringBootTest
public class InitTxTest {
@Autowired
Hello hello;
@Test
void go() {
// 초기화 코드는 스프링이 초기화 시점에 알아서 호출함
}
@TestConfiguration
static class initTxTestConfig {
@Bean
Hello hello() {
return new Hello();
}
}
@Slf4j
static class Hello {
@PostConstruct
@Transactional
public void initV1() {
boolean isActive = TransactionSynchronizationManager.isActualTransactionActive();
log.info("Hello init @PostConstruct tx active={}", isActive);
}
@EventListener(value = ApplicationReadyEvent.class)
@Transactional
public void initV2() {
boolean isActive = TransactionSynchronizationManager.isActualTransactionActive();
log.info("Hello init ApplicationReadyEvent tx active={}", isActive);
}
}
}
(1) @PostConstruct + @Transactional => 트랜잭션 적용 X

초기화 코드 먼저 호출 -> 그 다음에 트랜잭션 AOP 적용
-> 초기화 시점에는 트랜잭션을 획득할 수 X
(2) @EvnetListener(value = ApplicationReadyEvent.class) 사용

스프링이 컨테이너를 완전히 생성한 후 -> 이벤트가 붙은 메소드 호출
-> 트랜잭션 적용 O
4. 예외와 트랜잭션 커밋, 롤백
4-1. 예외와 트랜잭션 커밋, 롤백
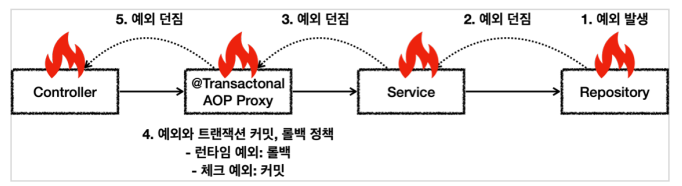
예외 발생 시, 내부에서 예외 처리 못하고, 트랜잭션 범위 밖으로 예외를 던질 때
스프링 트랜잭션 AOP는 예외의 종류에 따라 트랜잭션 커밋 or 롤백
- 런타임 예외 -> 트랜잭션 롤백
- 체크 예외 -> 트랜잭션 커밋
- 정상 -> 트랜잭션 커밋
1) 예외에 따른 트랜잭션 커밋, 롤백 테스트
package hello.springtx.exception;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.assertj.core.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.TestConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.*;
@SpringBootTest
public class RollbackTest {
@Autowired
RollbackService service;
@Test
void runtimeException() {
assertThatThrownBy(() -> service.runtimeException())
.isInstanceOf(RuntimeException.class);
}
@Test
void checkedException() {
assertThatThrownBy(() -> service.checkedException())
.isInstanceOf(MyException.class);
}
@Test
void rollbackFor() {
assertThatThrownBy(() -> service.rollbackFor())
.isInstanceOf(MyException.class);
}
@TestConfiguration
static class RollbackTestConfig {
@Bean
RollbackService rollbackService() {
return new RollbackService();
}
}
@Slf4j
static class RollbackService {
// 런타임 예외 발생 -> 롤백
@Transactional
public void runtimeException() {
log.info("call runtimeException");
throw new RuntimeException();
}
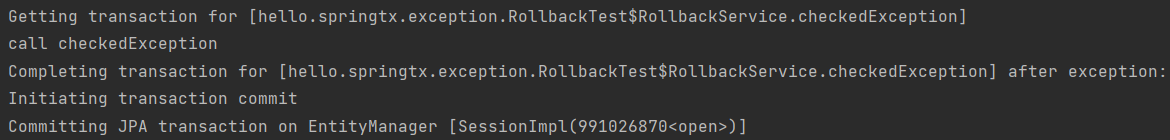
// 체크 예외 발생 -> 커밋
@Transactional
public void checkedException() throws MyException {
log.info("call checkedException");
throw new MyException();
}
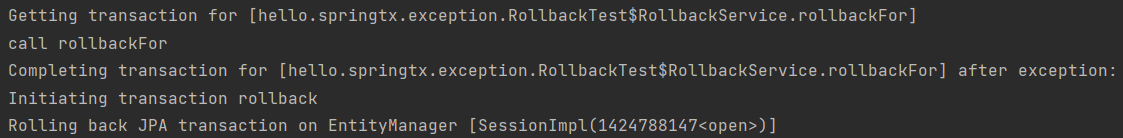
// 체크 예외 rollbackFor 지정 -> 롤백
@Transactional(rollbackFor = MyException.class)
public void rollbackFor() throws MyException {
log.info("call rollbackFor");
throw new MyException();
}
}
static class MyException extends Exception {
}
}
(1) 트랜잭션 확인 로그 추가
logging.level.org.springframework.transaction.interceptor=TRACE
logging.level.org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager=DEBUG
#JPA log
logging.level.org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager=DEBUG
logging.level.org.hibernate.resource.transaction=DEBUG
(2) 런타임 예외 -> 시스템 예외 -> 롤백
- 예) 복구할 수 없는 시스템 예외 -> 롤백

(3) 체크 예외 -> 비즈니스 예외 -> 커밋
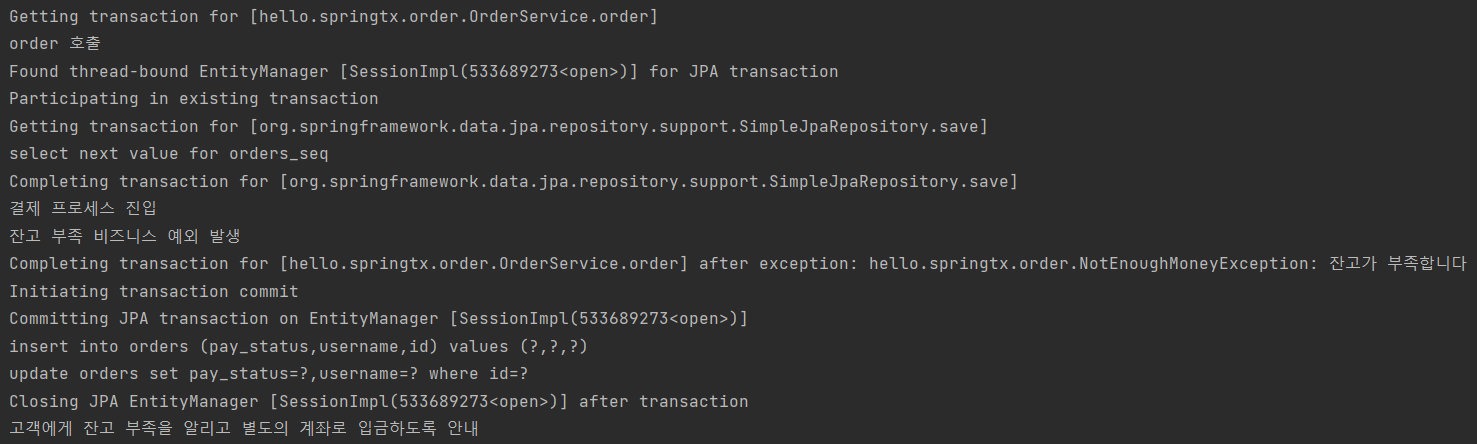
- 예) 비즈니스 의미가 있는 비즈니스 예외 -> 주문 시 잔고 부족 -> 일단 데이터 저장 후 커밋
(4) 체크 예외 rollbackFor 지정 -> 롤백
- 원래 체크 예외는 커밋인데, 롤백 하고 싶으면 지정 가능
4-2. 활용
* 비즈니스 요구사항
- 정상 : 데이터 저장, 결제 상태 = "완료" -> 커밋
- 시스템 예외 : 복구 불가능한 시스템 예외 -> 런타임 예외 -> 롤백
- 비즈니스 예외 : 데이터 저장, 결제 상태 = "대기" -> 체크 예외 -> 커밋
1) NotEnoughMoneyException - 잔고 부족 비즈니스 예외 (체크 예외)
package hello.springtx.order;
public class NotEnoughMoneyException extends Exception {
public NotEnoughMoneyException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
2) Order
package hello.springtx.order;
import jakarta.persistence.Entity;
import jakarta.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import jakarta.persistence.Id;
import jakarta.persistence.Table;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
@Entity
@Table(name = "orders")
@Getter
@Setter
public class Order {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String username; // 정상, 예외, 잔고부족
private String payStatus; // 대기, 완료
}- JPA를 사용하는 Order 엔티티
- ( * 실무에서 엔티티에 @Setter 사용 비추 )
- 테이블 이름 지정하지 않으면 클래스 이름인 order가 되지만, 데이터베이스 예약어(order by) 때문에 사용할 수 X -> orders라고 따로 지정
3) OrderRepository - 스프링 데이터 JPA 사용 (기본 CRUD)
package hello.springtx.order;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface OrderRepository extends JpaRepository<Order, Long> {
}4) OrderService
package hello.springtx.order;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Slf4j
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class OrderService {
private final OrderRepository orderRepository;
// JPA는 트랜잭션 커밋 시점에 Order 데이터를 DB에 반영한다.
@Transactional
public void order(Order order) throws NotEnoughMoneyException {
log.info("order 호출");
orderRepository.save(order);
log.info("결제 프로세스 진입");
if (order.getUsername().equals("예외")) {
log.info("시스템 예외 발생");
throw new RuntimeException("시스템 예외");
} else if (order.getUsername().equals("잔고부족")) {
log.info("잔고 부족 비즈니스 예외 발생");
order.setPayStatus("대기");
throw new NotEnoughMoneyException("잔고가 부족합니다");
} else {
log.info("정상 승인");
order.setPayStatus("완료");
}
log.info("결제 프로세스 완료");
}
}- 사용자 이름 = "예외"
- 시스템 예외 -> 런타임 예외 발생 -> 롤백
- 시스템 예외 -> 런타임 예외 발생 -> 롤백
- 사용자 이름 = "잔고부족"
- 비즈니스 예외 -> 체크 예외 발생 -> 커밋
- 비즈니스 예외 -> 체크 예외 발생 -> 커밋
- 사용자 이름 = 그 외
- 정상 -> 커밋
5) OrderServiceTest
package hello.springtx.order;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.assertj.core.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.Optional;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.*;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
class OrderServiceTest {
@Autowired
OrderService orderService;
@Autowired
OrderRepository orderRepository;
@Test
void complete() throws NotEnoughMoneyException {
// given
Order order = new Order();
order.setUsername("정상");
// when
orderService.order(order);
// then
Order findOrder = orderRepository.findById(order.getId()).get();
assertThat(findOrder.getPayStatus()).isEqualTo("완료");
}
@Test
void runtimeException() throws NotEnoughMoneyException {
// given
Order order = new Order();
order.setUsername("예외");
// when
assertThatThrownBy(() -> orderService.order(order))
.isInstanceOf(RuntimeException.class);
// then (시스템 예외 -> 롤백 -> 데이터가 없어야 함)
Optional<Order> orderOptional = orderRepository.findById(order.getId());
assertThat(orderOptional.isEmpty()).isTrue();
}
@Test
void bizException() {
// given
Order order = new Order();
order.setUsername("잔고부족");
// when
try {
orderService.order(order);
} catch (NotEnoughMoneyException e) {
log.info("고객에게 잔고 부족을 알리고 별도의 계좌로 입금하도록 안내");
}
// then
Order findOrder = orderRepository.findById(order.getId()).get();
assertThat(findOrder.getPayStatus()).isEqualTo("대기");
}
}
(1) JPA SQL 확인 로그 추가
#JPA SQL
logging.level.org.hibernate.SQL=DEBUG
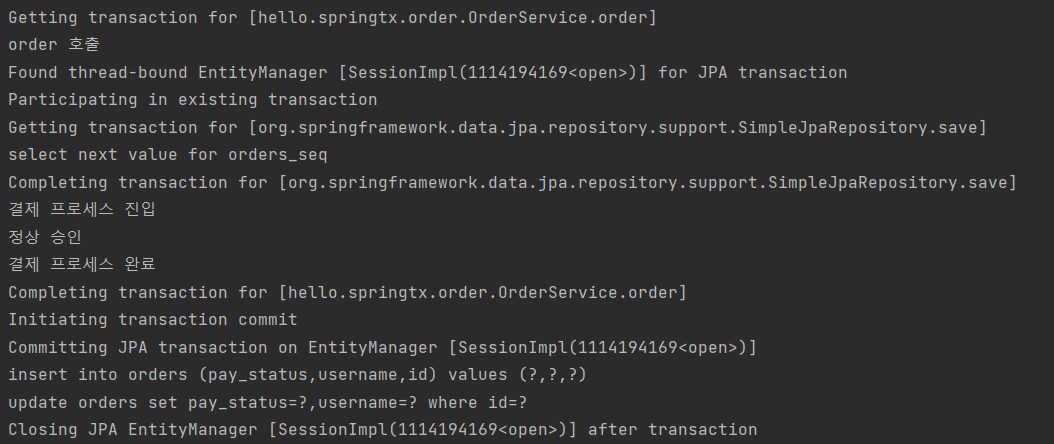
(2) complete() -> 정상 -> 커밋
- 커밋 시점에 데이터 insert, update
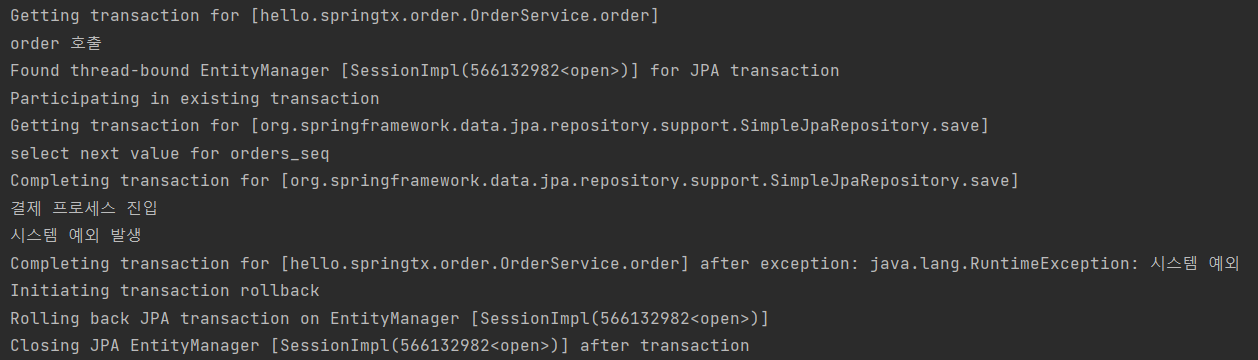
(3) runtimeException() -> 시스템 예외 -> 롤백
- 롤백이니까 insert 수행할 필요도 X
(4) bixException() -> 비즈니스 예외 -> 커밋
- 체크 예외 -> 커밋 수행 -> 데이터 insert, update 완
- 체크 예외인데 롤백하고 싶으면 -> rollbackFor 옵션 사용