[2022.09.08.목] 배열
while문
값을 순서대로 하나씩 제공하는 기능
제공할 값이 더이상 남아있는지 여부를 제공하는 기능 (boolean값 제공)
특정객체랑 같이 사용
그래서 while문은 그 특정 객체에 대해서 배울 때 배울거임
while문의 사용 예)
List<String> nameList = List.of("김유신", "강감찬", "이순신", "류관순");
Iterator<String> it = nameList.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
String name = it.next();
System.out.println(name);
}
* while문으로 반복작업을 수행할 대상객체는 Iterator<String>이다.
* hasNext()는 다음번에 수행할 대상이 남아있는지 확인하는 메소드
배열
1. 1차원 배열
하나의 변수로 여러 개의 값을 다룰 수 있다.

배열 생성하기
배열 생성할 때는 자료형의 기본값이 초기값으로 대입되어 있다.
정수의 디폴트 초기값: 0
실수의 디폴트 초기값: 0.0
문자열(객체)의 디폴트 초기값: null
문자의 디폴트 초기값: \u0000 (유니코드 젤 처음 값)
논리형의 디폴트 초기값: false
배열에 값 저장하기
arr1[0] = 34;
: 변수 arr1이 바라보는 배열객체의 주소값을 arr1 변수에 저장하고, 그 배열객체의 index 0번째에 정수값 34를 저장
arr2[3] = 3.14;
: 변수 arr2가 바라보는 배열객체의 주소값을 arr2 변수에 저장하고, 그 배열객체의 index 3번째에 실수값 3.14 저장
arr3[1] = "김유신";
: 변수 arr3이 바라보는 배열객체의 주소값을 arr3 변수에 저장하고, index 1번째에 문자열 "김유신"을 저장하는데
string 문자열도 객체이기 때문에 문자열 값을 직접 저장할 수 없고,
홍길동, 김유신 문자열이 들어있는 새로운 string 객체 생성 후,
배열객체가 그 각각의 string 객체를 참조
: arr3 변수에는 배열객체의 주소값, 배열객체의 한 칸에는 배열객체가 참조하는 String객체의 주소값
배열의 값 사용하기
System.out.println(arr1[0]); // 34
int sum = arr1[0] + arr1[1]; // int 기본형 변수이기 때문에 sum 변수에 정수값이 직접 저장됨
String name = arr3[1]; // String이 참조형이기 때문에 name 변수에는 arr[1]이 가리키는 객체의 주소값이 저장됨
1. 자료형과 크기를 지정해서 배열 생성하기
package day6;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArrayDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* 배열 객체 생성하기
*
* 1. 자료형과 크기를 지정해서 배열 생성하기
*
* 자료형[] 참조변수명 = new 자료형[크기];
* 예시)
* int[] arr1 = new int[5];
* double[] arr2 = new double[5];
* String[] arr3 = new String[3];
* * 배열객체에는 지정된 자료형의 값 혹은 주소값을 저장할 수 있는 연속된 저장소가 크기만큼 생성된다.
* * 각 저장소에는 자료형의 기본값이 초기값으로 대입되어 있다.
* * 기본값
* 정수: 0, 실수: 0.0, 문자: '\u0000', 불린: false, 그외는 전부 null
*
* 2. 배열 리터럴로 배열 생성하기
*
* 자료형[] 참조변수명 = {값, 값, 값, 값, 값};
* 예시)
* int[] arr1 = {90, 80, 60, 55, 100};
* double[] arr2 = {3.4, 4.1, 2.5, 4.5};
* Strign[] arr3 = {"김수영", "예빛", "한올", "치즈", "프롬", "김사월", "서자영"};
* * 값의 개수만큼 연속된 저장소가 있는 배열객체가 생성된다.
* * 각각의 저장소에는 순서대로 값들이 저장된다.
*
*/
int[]arr1 = new int[5];
double[] arr2 = new double[5];
String[] arr3 = new String[5];
arr1[0]=34;
arr1[1]=50;
arr2[3]=3.14;
arr2[4]=0.256;
arr3[0]="홍길동";
arr3[1]="김유신";
System.out.println("첫번째 배열의 값 출력하기");
// System.out.println(arr1[0]); //숫자만 바뀌니까 for문으로 가능
// System.out.println(arr1[1]);
// System.out.println(arr1[2]);
// System.out.println(arr1[3]);
// System.out.println(arr1[4]);
for(int index=0; index < 5; index++) { // <=4 라고 적지 않는다. 배열의 길이가 5
System.out.println(arr1[index]);
}
System.out.println("두번째 배열의 값 출력하기");
// System.out.println(arr2[0]);
// System.out.println(arr2[1]);
// System.out.println(arr2[2]);
// System.out.println(arr2[3]);
// System.out.println(arr2[4]);
for(int index=0; index<5; index++) {
System.out.println(arr2[index]);
}
System.out.println("세번째 배열의 값 출력하기");
// System.out.println(arr3[0]);
// System.out.println(arr3[1]);
// System.out.println(arr3[2]);
// System.out.println(arr3[3]);
// System.out.println(arr3[4]);
for(int index=0; index<5; index++) {
System.out.println(arr3[index]);
}
}
}첫번째 배열의 값 출력하기
34
50
0
0
0
두번째 배열의 값 출력하기
0.0
0.0
0.0
3.14
0.256
세번째 배열의 값 출력하기
홍길동
김유신
null
null
null
[34, 50, 0, 0, 0]
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 3.14, 0.256]
[홍길동, 김유신, null, null, null]
2. 배열 리터럴로 배열 생성하기
package day6;
public class ArrayDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] names = {"홍길동", "김유신", "이순신", "류관순", "강감찬", "윤봉길"};
int[] korScores = {100, 100, 60, 50, 80, 70};
int[] engScores = {90, 80, 50, 80, 70, 60};
int[] mathScores = {90, 70, 30, 70, 50, 60};
for(int index=0; index<6; index++) {
System.out.println(names[index]+"학생의 성적 조회");
System.out.println("이름: "+names[index]);
System.out.println("국어: "+korScores[index]);
System.out.println("수학: "+engScores[index]);
System.out.println("영어: "+mathScores[index]);
System.out.println();
}
}
}홍길동학생의 성적 조회
이름: 홍길동
국어: 100
수학: 90
영어: 90
김유신학생의 성적 조회
이름: 김유신
국어: 100
수학: 80
영어: 70
이순신학생의 성적 조회
이름: 이순신
국어: 60
수학: 50
영어: 30
류관순학생의 성적 조회
이름: 류관순
국어: 50
수학: 80
영어: 70
강감찬학생의 성적 조회
이름: 강감찬
국어: 80
수학: 70
영어: 50
윤봉길학생의 성적 조회
이름: 윤봉길
국어: 70
수학: 60
영어: 60
- 이름을 입력받아서 그 이름의 성적정보 출력하기 ( 개빡셈 !! )
package day6;
import utils.KeyboardReader;
public class ArrayDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] names = {"홍길동", "김유신", "이순신", "류관순", "강감찬", "윤봉길"};
int[] korScores = {100, 100, 60, 50, 80, 70};
int[] engScores = {90, 80, 50, 80, 70, 60};
int[] mathScores = {90, 70, 30, 70, 50, 60};
KeyboardReader reader = new KeyboardReader();
System.out.print("이름을 입력하세요.");
String value = reader.getString(); //입력받은 이름을 value에 저장함
int size = names.length; // 배열의 길이를 size에 저장함
boolean isExist = false; // 입력한 이름과 일치하는 학생이 있는지 없는지를 확인하는 변수.
int savedIndex = -1; // 이름이 배열의 몇번째에 있는지 확인하는 변수. 초기화를 0으로 하면, index 0번째 저장장소가 있어서 겹침
for(int index=0; index<size; index++) { // 1. 일치하는 이름의 인덱스 찾기
String name = names[index]; // names 배열의 n번째에 있는 이름을 name에 저장
if(name.equals(value)) { // index에 있는 name과 내가 입력한 value 비교
isExist = true; // 입력한 이름과 일치하는 학생 정보가 있으면 true
savedIndex = index; // 그 학생이 몇번째에 있는지
break; // break가 없으면 찾는 이름이 나온 이후에도 배열 크기만큼 계속 반복함
}
}
// 2. 일치하는 정보가 존재할 때 출력할 정보들
if(isExist) { // 한번도 실행 안했으면 초기화값 false인데, 한번 실행 했으니까 true로 남아있음
System.out.println("학생 성적정보가 존재합니다.");
String name = names[savedIndex];
int kor = korScores[savedIndex];
int eng = engScores[savedIndex];
int math = mathScores[savedIndex];
int total = kor + eng + math;
int average = total/3;
System.out.println("이름: "+name);
System.out.println("국어: "+kor);
System.out.println("영어: "+eng);
System.out.println("수학: "+math);
System.out.println("총점: "+total);
System.out.println("평균: "+average);
} else {
System.out.println("일치하는 성적정보가 존재하지 않습니다.");
}
}
}이름을 입력하세요.윤봉길
학생 성적정보가 존재합니다.
이름: 윤봉길
국어: 70
영어: 60
수학: 60
총점: 190
평균: 63
이름을 입력하세요.이성계
일치하는 성적정보가 존재하지 않습니다.
- 배열 이용해서 각 과목별 평균점수 구하기
package day6;
public class ArrayDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] names = {"홍길동", "김유신", "이순신", "류관순", "강감찬", "윤봉길"};
int[] korScores = {100, 100, 60, 50, 80, 70};
int[] engScores = {90, 80, 50, 80, 70, 60};
int[] mathScores = {90, 70, 30, 70, 50, 60};
// 각 과목별 평균점수 계산하기
// 국어점수 평균계산하기
int korTotalScore = 0;
for(int index = 0; index < korScores.length; index++) {
int score = korScores[index];
korTotalScore += score;
}
int korAverage = korTotalScore/korScores.length;
System.out.println("국어점수 총점: "+korTotalScore);
System.out.println("국어점수 평균: "+korAverage);국어점수 총점: 460
국어점수 평균: 76
- 향상된 for문 이용하기
처음부터 끝까지 추출할 때
package day6;
public class ArrayDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] names = {"홍길동", "김유신", "이순신", "류관순", "강감찬", "윤봉길"};
int[] korScores = {100, 100, 60, 50, 80, 70};
int[] engScores = {90, 80, 50, 80, 70, 60};
int[] mathScores = {90, 70, 30, 70, 50, 60};
/*
* Enhanced-for문 (향상된 for문)
* 형식
* 자료형[] 배열변수명 = {값1, 값2, 값3, 값4};
* for (자료형 변수명 : 배열변수명) {
* 수행문;
* }
* * 향상된 for문의 우항에는 배열/콜렉션(값이나 객체를 여러개 정하는 객체)을 참조하는 변수명이 위치한다.
* * 향상된 for문은 우항에 지정된 배열/콜렉션에 저장된 요소(값 혹은 객체)의 처음부터 끝까지 순서대로 데이터를 꺼낸다.
* * 향상된 for문은 우항에 지정된 배열/콜렉션에서 꺼낸 값을 좌항에 정의된 변수에 저장하고, 수행문을 실행하는 작업을 반복한다.
* * 향상된 for문을 사용하는 index를 사용하지 않고도 배열/콜렉션이 저장된 요소를 처음부터 끝까지 꺼낼 수 있다.
* * 추출된 값이 변수에 자동으로 저장되기 때문에 수행문에서는 변수에 저장된 값을 읽어서 연산에 활용할 수 있다.
*/
// 영어점수 평균 계산하기
int engTotalScore=0;
for (int score : engScores) { // 향상된 for문
engTotalScore += score;
}
int engAverage = engTotalScore/engScores.length;
System.out.println("영어점수 총점: "+ engTotalScore);
System.out.println("영어점수 평균: "+ engAverage);
//수학점수 평균 계산하기
int mathTotalScore = 0;
for(int score : mathScores) {
mathTotalScore += score;
}
int mathAverage = mathTotalScore/mathScores.length;
System.out.println("수학점수 총점: "+mathTotalScore);
System.out.println("수학점수 평균: "+mathAverage);
}
}영어점수 총점: 430
영어점수 평균: 71
수학점수 총점: 370
수학점수 평균: 61
- 배열 내의 최대값 최소값 구하기
최소값 : 1) int자료형의 최대값을 넣고 시작하기 (int의 최소값을 넣어버리면 얘가 항상 제일 작은 값이 되어버림)
(min) 2) 배열의 첫번째 값을 넣고 시작하기
최대값: 1) int자료형의 최소값을 넣고 시작하기 (int의 최대값을 넣어버리면 얘가 항상 제일 큰 값이 되어버림)
(max) 2) 배열의 첫번째 값을 넣고 시작하기
package day6;
public class ArrayDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] numbers = {20, 40, 10, 60, 3, 90, 21, 57, 84, 16};
// 배열의 값 중에서 가장 큰 값과 가장 작은 값을 알아내기
int min = 2_147_48_647; // int타입의 최대값 (int의 최소값으로 하면 얘가 항상 제일 작은값임)
int max = -2_147_483_648; // int타입의 최소값 (int의 최대값으로 하면 얘가 항상 제일 큰값임)
for(int value : numbers) { // numbers 배열에 있는 수를 순서대로 꺼내서 value에 저장
if (value < min) {
min = value;
}
if (value > max) {
max = value;
}
}
System.out.println("최소값: "+min);
System.out.println("최대값: "+max);
}
}최소값: 3
최대값: 90
- 성적이 1등인 학생의 점수, 평균 출력하기
package day6;
public class ArrayDemo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] names = {"홍길동", "김유신", "이순신", "류관순", "강감찬", "윤봉길"};
int[] korScores = {60, 30, 60, 50, 80, 70};
int[] engScores = {60, 80, 50, 80, 100, 60};
int[] mathScores = {60, 40, 30, 70, 90, 60};
// 시험성적이 1등인 학생의 이름, 국어, 영어, 수학, 총점, 평균을 출력하기
int maxTotalScore = 0; // 0이 점수중에서 제일 최저 점수니까
int topScoreIndex = -1; // 해당하는 한 사람의 정보를 여러개 꺼내야 하니까 index 이용하는게 좋음
for(int index=0; index<names.length; index++) {
int kor = korScores[index];
int eng = engScores[index];
int math = mathScores[index];
int totalScore = kor + eng + math;
if (totalScore > maxTotalScore) {
maxTotalScore = totalScore;
topScoreIndex = index; // 가장 높은 사람의 인덱스를 추출했음
}
}
String name = names[topScoreIndex];
int kor = korScores[topScoreIndex];
int eng = engScores[topScoreIndex];
int math = mathScores[topScoreIndex];
int totalScore = kor + eng + math;
int average = totalScore / 3;
System.out.println("이름: "+name);
System.out.println("국어: "+kor);
System.out.println("영어: "+eng);
System.out.println("수학: "+math);
System.out.println("총점: "+totalScore);
System.out.println("평균: "+average);
}
}이름: 강감찬
국어: 80
영어: 100
수학: 90
총점: 270
평균: 90
- 내가 푼거
String[] names = {"홍길동", "김유신", "이순신", "류관순", "강감찬", "윤봉길"};
int[] korScores = {60, 30, 60, 50, 80, 70};
int[] engScores = {60, 80, 50, 80, 100, 60};
int[] mathScores = {60, 40, 30, 70, 90, 60};
// 시험성적이 1등인 학생의 이름, 국어, 영어, 수학, 총점, 평균을 출력하기
// 총점 kor+eng+math 1등 (max) 구하기
int max= 0;
int savedIndex= -1;
for(int index=0; index<names.length; index++) { //총점이 가장 높은 학생의 인덱스를 구하기
int kor = korScores[index];
int eng = engScores[index];
int math = mathScores[index];
int total = kor + eng + math;
if(total>max) {
max= total;
savedIndex=index;
}
}
String name = names[savedIndex]; //1등인 학생의 정보 출력하기
int kor = korScores[savedIndex];
int eng = engScores[savedIndex];
int math = mathScores[savedIndex];
int total = kor + eng + math;
System.out.println("이름: "+name);
System.out.println("국어: "+kor);
System.out.println("영어: "+eng);
System.out.println("수학: "+math);
System.out.println("총점: "+total);
2. 2차원 배열
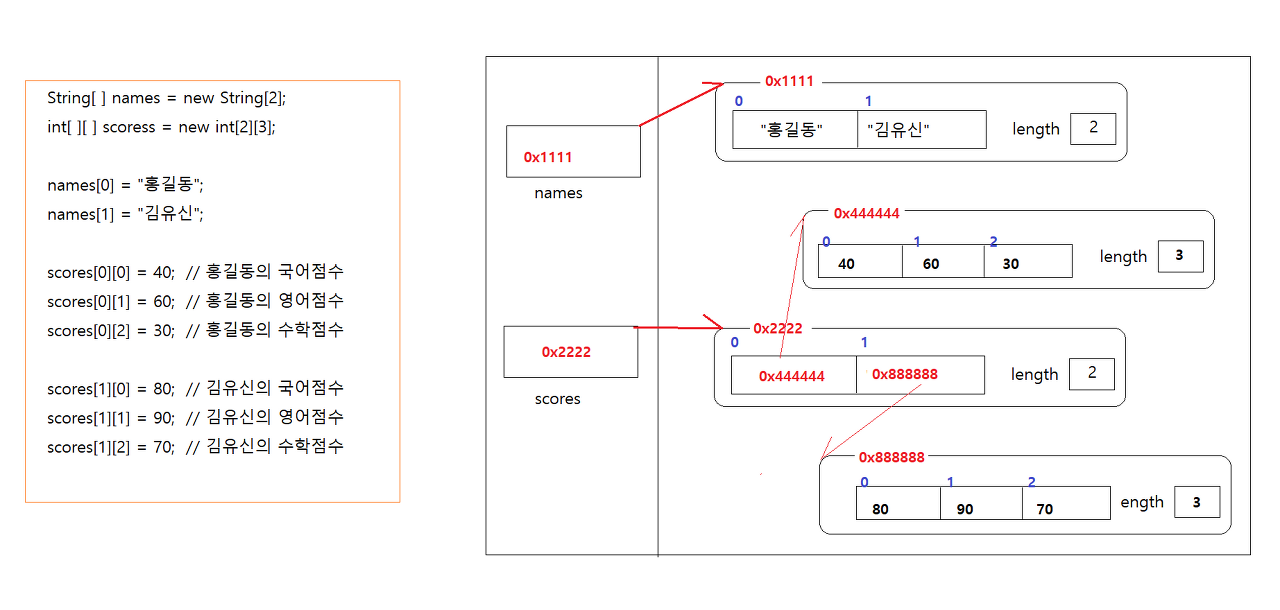
- 2차원배열에 저장된 값 출력하기
package day6;
public class ArrayDemo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* 1차원배열과 다차원배열
* 1차원배열
* 자료형[] 변수명 = new 자료형[크기];
* 자료형[] 변수명 = {값, 값, 값, 값};
*
* 2차원배열
* 자료형[][] 변수명 = new 자료형[크기][크기];
* 자료형[][] 변수명 = {{값, 값, 값}, {값, 값, 값}, {값, 값, 값}};
*/
// 2차원배열 생성하기
int[][] scores = new int[2][3]; // 2행3열
// 2차원배열에 값 저장하기
scores[0][0] = 40;
scores[0][1] = 60;
scores[0][2] = 30;
scores[1][0] = 80;
scores[1][1] = 90;
scores[1][2] = 70;
// index를 사용해서 2차원배열에 저장된 값 출력하기
for (int i=0; i<2; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<3; j++) {
System.out.print(scores[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
// 향상된 for문을 사용해서 2차원배열에 저장된 값 출력하기
for(int[] row : scores) { // scores에서 꺼낸 정수배열을 배열타입(int[])의 변수 row에 저장
for(int value : row) { // scores[0]에서 꺼낸 정수 0,1,2 중 하나를 정수타입(int)의 변수 value에 저장
System.out.print(value+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}40 60 30
80 90 70
40 60 30
80 90 70
- 배열객체

scores : 0x2222 객체를 참조하는 변수 = int배열을 여러개 가지고 있는 int[ ][ ] ( int배열의 배열 )
scores[0] : 0x4444(int배열)을 참조하는 변수 = int를 여러개 가지고 있는 int[ ] 타입 (int배열)
scores[1]: 0x8888(int배열)을 참조하는 변수 = int를 여러개 가지고 있는 int[ ] 타입 (int배열)
따라서 scores에서 하나를 꺼내면 -> 정수배열을 꺼내는 것!
for(int[ ] row : scores) { // scores에서 꺼낸 정수배열을 배열타입(int[ ])의 변수 row에 저장
for(int value : row) { // scores[0]에서 꺼낸 정수 0,1,2 중 하나를 정수타입(int)의 변수 value에 저장